The IIT has released the GATE exam format. This format shows how the exam is structured. It’s important for those who want to do well on the exam. The GATE exam is a computer-based test that lasts 3 hours. It’s offered by IIT for 30 different fields in engineering, technology, and science. People should look at the full exam format before they sign up for the GATE exam.
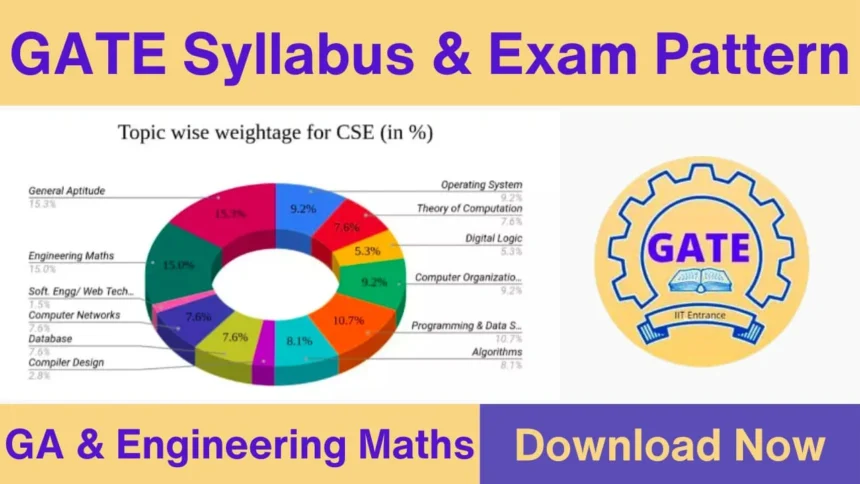
The GATE exam has three main parts: General Aptitude, Engineering Mathematics, and a specific subject. There are 65 questions worth 100 marks. General Aptitude is worth 15 marks. In some exams, Engineering Mathematics is worth 13 marks, and the subject is worth 72 marks. In other exams, there’s no Engineering Mathematics, so General Aptitude is worth 15 marks and the subject is worth 85 marks. You can find more information about the GATE Syllabus and marking scheme on this page.
Highlights of GATE Examination Syllabus
| Nodal Authority | Indian Institute of Technology |
| Exam Name | Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering |
| Number of Questions | 10 (GA) + 55 (subject) = 65 Questions |
| Total Marks | 100 |
| Marking Scheme | Questions carry 1 mark and 2 marks |
| Official Website | iitr.ac.in |
Pattern of Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering
The GATE exam has 65 questions worth 100 marks. 10 of these questions are about general knowledge and are worth 15 marks. The rest of the questions are about different subjects. For most subjects, 28 marks are for general knowledge and math, and 72 marks are for the subject. But for some subjects, 15 marks are for general knowledge, and 85 marks are for the subject.
The GATE exam now lets you choose two subjects. You need to be careful when picking them because one will be your main subject and the other has to be from a list of subjects that go with your main one. You can find out which subjects are allowed in the second paper later on this page.
GATE Examination Marking Scheme
The GATE exam has 65 questions that add up to 100 points. There are three different kinds of questions: MCQs, MSQs, and NATs. Candidates should know how each type of question works and how points are given for each one.
For Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
- Each MCQ can be worth one or two marks across all GATE papers.
- A quartet of choices will be provided for every MCQ.
- Incorrect answers in MCQs attract a penalty, deducting one-third of the points designated for that question.
Regarding Multiple Select Questions (MSQs):
- Like MCQs, MSQs carry one or two marks on every GATE paper.
- Each MSQ will present four choices from which to select.
- MSQs do not impose negative scoring for wrong responses.
- Scoring for MSQs will be adjusted based on the level of accuracy relative to the other choices.
For Numerical Answer Type (NAT) Questions:
- NAT questions are valued at one or two marks across all GATE examinations.
- Unlike MCQs and MSQs, NAT questions won’t offer multiple-choice options.
- Participants are required to enter their responses as real numbers through a virtual keyboard provided during the GATE examination.
- No penalties are applied for incorrect responses in NAT questions.
Category of Questions in GATE Exam
Applicants should understand that the GATE exam tests their skills in different ways. Here are the specific things the exam will look for.
- Remember, these questions ask you to use specific facts, ideas, or rules that you’ve learned. You’ll need to answer the questions by thinking about what you already know, or by doing a little bit of math.
- These questions test the applicant’s understanding of simple ideas and their ability to draw easy conclusions from them.
- This part of the test checks how well you can use what you know to solve problems. You’ll need to use math or logic to figure things out.
- Analytical and creative thinking questions ask you to use your skills to look closely at information, like pictures or charts, and find answers. You might need to compare different pieces of information or figure out what’s important and what’s not.
GATE Paper-wise Marks Distribution
For the GATE examination, consult the following summary to understand the marking distribution across different subjects. This information is concisely tabulated for easy reference.
| Paper Code | GA Marks | Subject Marks | Total Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE, AG, BM, BT, CE, CH, CS, EC, EE,ES, IN, ME, MN, MT, NM, PE,PI, TF, | 15 | Engineering Math (13 marks)Specific subject (72 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| CY, DA, EY, MA, PH, ST | 15 | 85 | ||
| AR [Part A + Part B1 or B2(B1: Architecture or B2: Planning)] | 15 | Part A (60 marks)Part B1/ B2 (25 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| GE [Part A + Part B (Section I or Section II) | 15 | Compulsory Part A (55 marks)Part B1/ B2 (30 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| GG [Part A + Part B (Section 1: Geology orSection 2: Geophysics)] | 15 | Compulsory Part A (25 marks)Part B1/ B2 (60 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| XE (Section A + Any Two Sections) | 15 | Compulsory section A (15 marks)Add. Section 1 (35 marks)Add. Section 2 (35 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| XH (Section B1 + Any One Section) | 15 | Compulsory section B1 (25 marks)Additional section (60 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |
| XL (Section P + Any Two Sections) | 15 | Compulsory section A (25 marks)Add. Section 1 (30 marks)Add. Section 2 (30 marks) | 100 | 180 Mins |